—— Liver cancer ——
Liver cancer refers to malignant tumors that breed in the liver or start from the liver. They are mainly divided into two categories: primary liver cancer and secondary liver cancer. Tracing the root causes, the continuous invasion of hepatitis B and hepatitis C viruses, or the cirrhosis caused by long-term alcoholism, is like cultivating a "vegetable ground" for the breeding of liver cancer.
Focusing on the domestic situation, liver cancer has become one of the most common cancers among men and women in my country, ranking at the forefront of the "ranking" of various types of cancers. In 2020 alone, the total number of liver cancer cases reported nationwide was as high as [X]. Behind these numbers are the health challenges faced by countless families.
When the haze of middle and late stage liver cancer is shrouded in, the patients and their families are filled with anxiety and helplessness. The most worrying question is: Can it be cured?
The progress of modern medicine has brought hope to patients, among which minimally invasive technology stands out with its unique advantages. This technology has tiny incisions and minimal trauma to the body, which can almost be called a "gentle" touch; the side effects are also greatly reduced, avoiding the pain of hair loss, vomiting and weakness caused by traditional radiotherapy and chemotherapy. With these advantages, minimally invasive technology can not only avoid large-scale surgical resection, but also effectively prolong the survival of patients and improve their quality of life, bringing new hope to patients with mid- and late-stage liver cancer.
For more cancer knowledge, please click online doctor for consultation
——Classification of liver cancer——
There are various classification methods for liver cancer, and they vary from different angles:
● Classification by pathological characteristics:
Diffuse type: The cancerous tissue is diffusely distributed in the liver, and the boundary between the surrounding liver tissue is unclear.
Block type: The diameter of the cancer is generally greater than 5cm, and it is a single or multiple fused block, with a hard texture.
Nodule type: The diameter of the cancerous nodules is usually below 5cm, and multiple nodules are scattered in the liver.
Small cancer type: The diameter of a single cancer nodule does not exceed 3cm, or the sum of the diameters of two adjacent cancer nodules is less than 3cm.
● Classification by encapsulation, cirrhosis and portal venous thrombosis:
Invasive liver cancer: The cancerous tissue has invasive growth of surrounding liver tissue, no obvious envelope, and often coexist with cirrhosis, and portal venous thrombosis is prone to occur in the early stage.
Expanded liver cancer: The tumor shows expansive growth, has a complete or relatively complete envelope, has clear boundaries from surrounding tissues, has a relatively mild degree of combined cirrhosis, and portal venous thrombosis occurs later.
Infiltrating and inflatable liver cancer: It has both infiltrating and inflatable characteristics. Some areas of the tumor grow in infiltrating and some areas grow in inflatable.
Diffuse liver cancer: The cancer tissue is widely distributed throughout the liver, and the liver is enlarged and deformed, often accompanied by severe cirrhosis, and the incidence of portal venous thrombosis is high.
Special types of liver cancer: including rare types such as fibroplanar layer carcinoma and clear cell carcinoma, with unique pathological and clinical characteristics.
● Classification by organizational source:
Hepatocellular liver cancer: Most common, it is malignant from hepatocytes, accounting for about 90% of primary liver cancer.
Intrahepatic bile duct liver cancer: originates from intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells, with a relatively low incidence, and its pathological and biological characteristics are different from hepatocellular liver cancer.
Mixed liver cancer: It contains both hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma, which is relatively rare.
—— Traditional treatment technology for liver cancer ——
Traditional treatments for liver cancer
Surgery: Surgery is used to remove cancerous tissue and any lymph nodes in the neck that may have metastasized.
Radiation therapy: It can be used as a single treatment or combined with other treatments such as surgery or chemotherapy.
Chemotherapy: often used as palliative treatment for advanced cancer that is inoperable or has distant metastasis;
—— New technology for fighting liver cancer ——
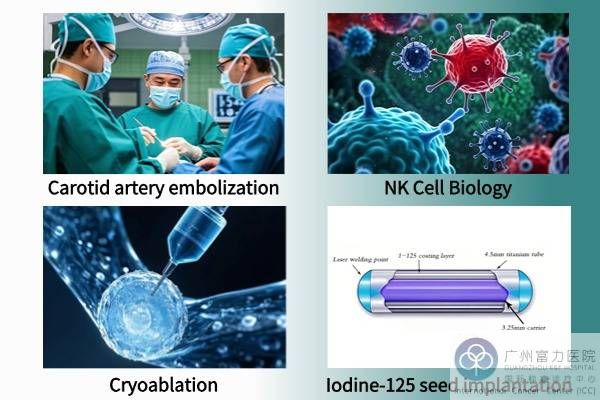
What is transarterial embolization?
Transarterial embolization is a minimally invasive technique that "starves the tumor to death." Under the guidance of DSA (digital subtraction angiography), the physician inserts the catheter into the tumor-supplying artery through femoral artery puncture (only a 2mm incision) and injects embolic agents (such as drug-loaded microspheres and iodized oil) to block blood flow. The tumor necroses due to ischemia and hypoxia, while the surrounding normal tissues are almost intact. If combined with chemotherapy drugs (i.e. TACE), a double blow of "cutting off food supply + poisoning" can be achieved simultaneously, and the efficacy can be increased by 2-3 times. It is done under local anesthesia, leaving only tiny pinholes in the skin.
What is NK cell biological immunotherapy?
NK cells (natural killer cells) are the "vanguard" of the human immune system. They can quickly identify and destroy cancer cells and abnormal cells infected by viruses without having to "remember" the enemy in advance.
What is cryoablation?
Cryoablation is a minimally invasive technique that physically destroys tumors through "extremely low temperatures". Under the guidance of CT or ultrasound, the doctor accurately punctures a pen-thin ablation needle into the tumor and releases argon gas to instantly cool the tumor to -140℃~196℃. The extremely cold environment freezes cancer cells into ice crystals, and the cell structure completely collapses. Subsequently, the helium gas is quickly heated to 20°C~40°C, and the alternating hot and cold "temperature difference attack" further destroys the residual cancer cells without damaging the surrounding normal tissues.
What is iodine-125 seed implantation?
Iodine-125 seeds are a type of "mini-radiotherapist" that is only 4.5 mm in size and contains the radioactive isotope iodine-125. After accurately locating the tumor using imaging technology (such as CT), doctors use a fine needle to implant dozens to hundreds of iodine-125 particles into the tumor. These particles deliver low-dose radiation over a continuous period of time (about 6 months), directly destroying tumor cells while maximizing the protection of surrounding normal tissue.
In addition, we also have the following tumor elimination technologies:
Radiofrequency ablation, cytokine therapy, CAR-T cell therapy, microwave ablation, immune checkpoint inhibitor PD-1/PD-L1 therapy, monoclonal antibody therapy...
—— Enter the technology area to see which technology is more suitable for you
—— Liver cancer patient story ——

Nguyen Thi Phuong (Vietnamese patient)
"Life should not be limited by geography. As long as you don't give up looking for hope, you can rekindle the light of life even across borders...."
—— To find out how she recovered, read his story
—— Symptoms of liver cancer ——
Symptoms of liver cancer:
Significant loss of appetite
Dull pain in the right upper abdomen
Bleeding tendency
Systemic symptoms
Jaundice, ascites and skin itching
Experts remind: Some typical symptoms of liver cancer usually appear when the disease progresses to the middle and late stages. Go to the hospital for relevant examinations as soon as possible. Early detection and early treatment are extremely important to prolong the survival time and improve the quality of life of liver cancer patients.
—— For more cancer knowledge, please click on the online doctor for consultation.
—— Liver cancer diagnosis ——
Commonly used clinical methods for diagnosing liver cancer:
Ultrasound examination
CT
MRI
Alpha-fetoprotein test
Selective celiac or hepatic artery imaging
If a reasonable and effective treatment plan can be formulated and implemented in the early stages, patients with early liver cancer are very likely to achieve long-term survival.
—— Enter the diagnostic center to learn about the latest diagnostic and treatment technologies
Use precise technology to create more possibilities for life.
The Cancer Center of Guangzhou R&F Hospital has opened an era of "chemotherapy-free survival" for cancer patients, winning a lasting victory for life. If you or your family are facing difficulties in cancer treatment, please contact the Guangzhou R&F Hospital Cancer Center. We offer multilingual medical history consultations, contact us today to get an assessment of your treatment eligibility.
Contact Us:
email: rfcancercenter@gmail.com |
WhatsApp: +86 18565157271