Causes of Liver Cancer
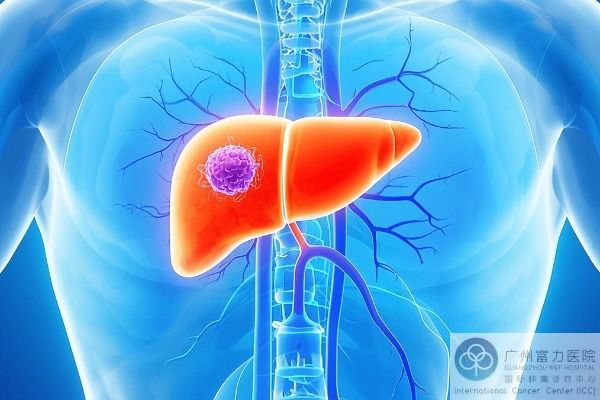
Liver cancer: a hidden "health killer" and new hope for treatment
Liver cancer is like a "time bomb" lurking in the body. It refers to a malignant tumor that grows in the liver or starts in the liver. It is mainly divided into two categories: primary liver cancer and secondary liver cancer. To trace the root cause, the continuous invasion of hepatitis B and C viruses, or cirrhosis caused by long-term alcoholism, is like a "breeding ground" for the growth of liver cancer, putting the liver into crisis step by step.
Focusing on the current domestic situation, the severity of liver cancer cannot be underestimated. According to relevant statistics, it has become one of the more common cancers among men and women in my country, and ranks at the top of the "ranking list" of various cancers. In 2020 alone, the total number of liver cancer cases reported nationwide reached [X] cases. Behind these numbers are health challenges faced by countless families.
When the shadow of late-stage liver cancer looms, patients and their families are filled with anxiety and helplessness. The most worrying question is: Can it still be cured? Fortunately, advances in modern medicine are dispelling this haze. Minimally invasive technology has emerged with its unique charm. It is like a delicate "scalpel" with tiny incisions, and the trauma to the body is almost a "gentle" touch; the side effects are extremely small, allowing patients to say goodbye to the painful tortures such as hair loss, vomiting, weakness, etc. brought by traditional radiotherapy and chemotherapy. With these advantages, minimally invasive technology can not only cleverly avoid drastic surgical resection, but also effectively prolong the patient's survival. It also allows them to regain confidence in life and improve their quality of life during the fight against cancer, lighting the light of hope for patients with mid- and late-stage liver cancer.
Classification of liver cancer:
There are many ways to classify liver cancer, and they are different from different perspectives:
● Classification by pathological characteristics:
Diffuse type: Cancerous tissue is diffusely distributed in the liver, with unclear boundaries with surrounding liver tissue.
Massive type: The diameter of the tumor is generally larger than 5 cm, and it appears as a single or multiple fused masses with a hard texture.
Nodular type: The diameter of cancerous nodules is usually less than 5 cm, and multiple nodules are scattered in the liver.
Small cancer type: the diameter of a single cancer nodule does not exceed 3cm, or the sum of the diameters of two adjacent cancer nodules is less than 3cm.
● Classification based on capsule, liver cirrhosis and portal vein tumor thrombosis:
Invasive liver cancer: The cancer tissue grows infiltratingly into the surrounding liver tissue without an obvious capsule. It often coexists with cirrhosis and portal vein tumor thrombosis is prone to occur in the early stages.
Expansive liver cancer: The tumor grows in an expansive manner, has a complete or relatively complete capsule, and is clearly demarcated from surrounding tissues. The degree of liver cirrhosis is relatively mild, and portal vein tumor thrombus appears later.
Invasive expansive liver cancer: It has the characteristics of both invasive and expansive types, with some areas of the tumor growing invasively and some areas growing expansively.
Diffuse liver cancer: Cancerous tissue is widely distributed throughout the liver, causing the liver to become enlarged and deformed, often accompanied by severe cirrhosis, and a high incidence of portal vein tumor thrombosis.
Special types of liver cancer: including rare types such as fibrolamellar carcinoma and clear cell carcinoma, which have unique pathological and clinical characteristics.
● Classification by organizational source:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: The most common type, arising from the malignancy of hepatocytes, accounting for about 90% of primary liver cancer.
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: It originates from the intrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells, has a relatively low incidence, and its pathological and biological characteristics are different from those of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Mixed liver cancer: contains both hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma components, which is relatively rare.
The causes of liver cancer are complex and are usually the result of multiple factors working together. The following are the main known causes and risk factors:
1. Chronic viral hepatitis
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection: HBV infection is one of the main causes of liver cancer. Long-term infection can lead to cirrhosis, which in turn increases the risk of liver cancer.
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection: HCV infection is also an important cause of liver cancer. Chronic infection can lead to liver fibrosis and cirrhosis.
2. Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis: Regardless of the cause of cirrhosis (such as viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease), it is an important risk factor for liver cancer.
3. Alcoholic liver disease
Long-term heavy drinking: Alcohol can directly damage liver cells, leading to alcoholic hepatitis, liver fibrosis and cirrhosis, thereby increasing the risk of liver cancer.
4. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Obesity and metabolic syndrome: NAFLD is closely related to metabolic syndromes such as obesity, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. It may develop into non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and cirrhosis, increasing the risk of liver cancer.
5. Aflatoxin Exposure
Aflatoxin: A strong carcinogen produced by mold, commonly found in moldy peanuts, corn and other foods. Long-term intake may increase the risk of liver cancer.
6. Genetic factors
Family history: People with a family history of liver cancer have a higher risk of the disease, which may be related to genetic susceptibility.
Genetic metabolic diseases: such as hemochromatosis, α1-antitrypsin deficiency, etc., may increase the risk of liver cancer.
7. Other liver diseases
Autoimmune hepatitis: Long-term inflammation may lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC): A chronic liver disease that may increase the risk of liver cancer.
8. Environmental and occupational exposure
Chemicals: Long-term exposure to chemicals such as arsenic and vinyl chloride may increase the risk of liver cancer.
Radiation exposure: Long-term exposure to high doses of radiation may increase the risk of disease.
9. Lifestyle
Smoking: Carcinogens in tobacco may affect the liver through blood circulation.
Unhealthy diet: A high-fat, high-sugar diet may indirectly increase the risk of liver cancer.
10. Molecular Mechanism
Gene mutation: Gene mutations such as TP53 and CTNNB1 may be involved in the occurrence of liver cancer.
Epigenetic changes: Epigenetic changes such as DNA methylation and histone modification may also be related to liver cancer.
Precautions
Vaccination: Vaccination with hepatitis B vaccine can effectively prevent HBV infection.
Antiviral treatment: Patients with chronic hepatitis B or C should receive standardized treatment to reduce the risk of liver cancer.
Avoid alcohol: Limiting alcohol intake can help prevent alcoholic liver disease.
Eat a healthy diet: Avoid eating moldy foods to reduce exposure to aflatoxin.
Weight control: Prevent obesity and metabolic syndrome through healthy diet and exercise.
Regular screening: High-risk groups (such as patients with chronic hepatitis and cirrhosis) should undergo regular liver ultrasound and AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) tests.
Summarize
The causes of liver cancer involve multiple factors including viral hepatitis, cirrhosis, alcohol, aflatoxin, and genetics. The risk of liver cancer can be effectively reduced by preventing infection, improving lifestyle and early screening.
If you have further questions, please consult a professional doctor.
Use precise technology to create more possibilities for life.
The Cancer Center of Guangzhou R&F Hospital has opened an era of "chemotherapy-free survival" for cancer patients, winning a lasting victory for life. If you or your family are facing difficulties in cancer treatment, please contact the Guangzhou R&F Hospital Cancer Center. We offer multilingual medical history consultations, contact us today to get an assessment of your treatment eligibility.
Contact Us:
email: rfcancercenter@gmail.com |
WhatsApp: +86 18565157271